8,000 years ago, a star 20 times more massive than our Sun went KABOOM ...
If you said Kaboom in the voice of Marvin the Martian, then we think alike. Trying something new with this blog post. Going to change the order of the content. Let me know what you think. Note: An AI tool was used to help write the text in the "What is it?" section.
On 7/3/2025, I captured this image of the Cygnus Loop from my backyard with my wide-field imaging rig.
 |
| A wide-field image of the Cygnus Loop captured from my backyard on 7/3/2025. |
When processing Astro photos, it is common practice to separate the stars from the image. The stars and the object are then processed separately and recombined at the end. Here is the Starless image used to create the final image above.
 |
| A starless version of the image used in the processing of this data. |
What is it?
 |
| An annotated image of the Cygnus Loop. |
Western Veil Nebula (NGC 6960 “Witch’s Broom”)
Located at the western edge of the Cygnus Loop, NGC 6960 is
a tangle of glowing filaments spanning over a degree of sky. Also called the
Witch’s Broom, its curved arc traces shock waves from a supernova that exploded
roughly 8,000 years ago, heating and ionizing the interstellar gas. Bright
knots and wisps of hydrogen- and oxygen-rich material alternately glow in red
and teal, against a field of faint Milky Way stars.
Eastern Veil Nebula (NGC 6992, NGC 6995 & IC 1340)
This section consists of two main filamentary loops—NGC 6992
to the north and NGC 6995 immediately south—plus fainter outlying strands
cataloged as IC 1340. The sinuous, lace-like structures mark where fast-moving
debris slams into surrounding gas at hundreds of kilometers per second. Vivid
filament edges glow in narrowband emissions, revealing intricate curlicues of
supernova-heated plasma.
Open Star Cluster NGC 6940
Situated just south of the Eastern Veil, NGC 6940 is a rich
grouping of several dozen 8th–10th magnitude stars. At about 2,500 light-years
distance, this intermediate-age cluster (≈1 billion years) provides a
contrasting backdrop of yellow-white suns set against the nebular filaments.
Its loosely bound stars form a gentle arc, adding depth to the wide-field
composition.
Foreground and Field Stars
- 52
Cygni: A 4th-magnitude star superimposed on the Western Veil’s arc,
lending the Witch’s Broom its bright “handle.”
- 49
Cygni & 48 Cygni: Pair of 5th-magnitude stars near the Eastern Veil,
framing the nebular loops.
- Countless
fainter Milky Way stars fill the background, emphasizing the vastness of
the supernova remnant.
Together, these objects showcase the aftermath of stellar death alongside ongoing stellar life, framed by a tapestry of stars in the rich Cygnus Milky Way.
How Big is it?
The Cygnus Loop has a size of 3 degrees on the night sky and is about 120 light years across. For comparison, the Sun and the Moon have an angular distance of about 1/2 of a degree.
The Western Veil Nebula (NGC 6960) has a size of 70 x 6 arcminutes (1 degree is 60 arcminutes) on the night sky and is about 53.1 light years across.
The Eastern Veil Nebula (NGC 6992) has a size of 60 x 30 arcminutes (1 degree is 60 arcminutes) on the night sky and is about 45.5 light years across.
NGC 6940 has a size of 25 arcminutes (1 degree is 60 arcminutes) on the night sky and is about 18.3 light years across.
How Far is it?
The entire Cygnus Loop (including Eastern & Western Veil Nebulae) is located about 2,100 light-years (ly) in the Constellation Cygnus.
NGC 6940 is located about 2,500 light-years (ly) in the Constellation Cygnus.
How to Find it?
This object can be visually observed. Dark skies are a must. A nebula filter, specifically an Oiii filter are almost required. This is a large object, so a wider field of view will let you see more of the object.
In the Finder Chart below. Find Cygnus the Swan, then locate Gienah (Epsilon Cygni) indicated by the letter "A" and Zeta Cygni indicated by the letter "B". Both stars will form an imaginary triangle with 52 Cygni, indicated by the letter "C". 52 Cygni is the bright star in the Western Veil.
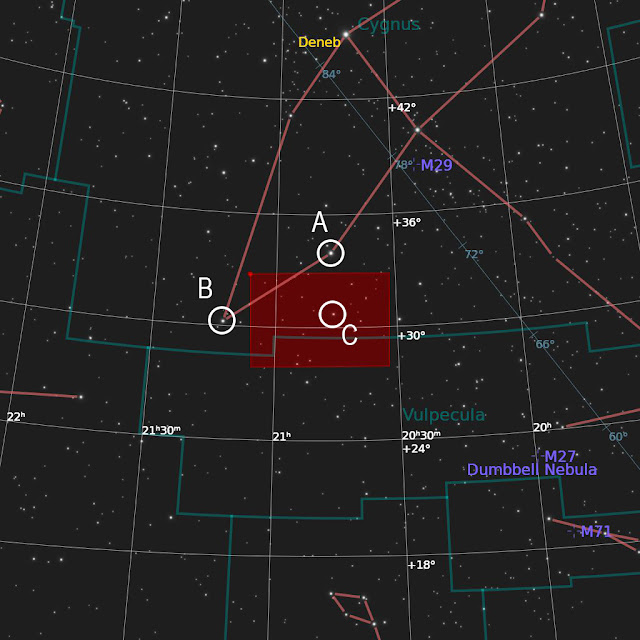 |
| Finder Chart for the Cygnus Loop |
Imaging Notes:
Thursday July 3rd was forecast to be clear at
night. I had a vacation day, extending the Independence Day holiday weekend. A
clear night, no work the next day, no question I would be imaging. The 3rd
was one day past 1st Quarter Moon, so a bright Moon would be up all
night. Therefore, I decided to go after the Cygnus Loop with my wide-field
setup and dual narrowband filter. I had to wait until nearly midnight for the
object to clear the trees to begin the imaging sequence. The first sub came in
at 11:46 PM. Subs continued to roll in until 4:14 AM as the skies started to
brighten as dawn approached. Overall, an eventful evening. The skies were
really good, and the equipment behaved.
Processing:
All pre and post processing was performed in PixInsight. Pre-Processing: All subs were visually inspected with Blink and subs with issues were removed. All light Frames, Flats, Darks and Dark flats were loaded into WBPP. Linear Post Processing: Background extraction was performed with GraXpert followed by BXT (correct only). SPCC was used for Color Calibration followed by a full application of BXT. The Stars were removed using StarXT. Starless Linear: Noise was reduced with NXT. The image was made non-linear with HT. Linear Stars: The stars were made non-linear with Seti Astro's Star Stretch Script.
Non-linear Post Processing: Starless: Color, intensity, and contrast were adjusted with various applications of CT. Saturation was increased with CT. The Image blend Script was used to sharpen the image with a High Pass Filter. LHE was applied at 2 Kernel sizes and Unsharp mask was applied. CT was used to increase contrast. Stars: Saturation was increased with CT. SCNR was applied and the Correct Magenta Stars Script was used to help with stars captured with a dual narrowband filter. CT was used to adjust contrast one last time. Final: The Stars and Starless images were combined with Pixel Math to produce the final image.

































